Sectors
Environmental
The environmental industry sector has been the fastest growing industry sector in the world over the last 40 years, as the world comes to terms with the need to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels.
Environmental Sustainability
Environmental sustainability covers a wide range of issues starting from a specific location to global. Global issues comprise concerns about GHG mitigation, climate change, and renewable energy, while the location-specific issues are soil erosion, water management, soil quality, and air and water pollution.
The role of biofuel in the dimension of environmental sustainability is largely to reduce GHG emissions (e.g., CO2, methane, N2O), though there are controversies regarding its effectiveness. The leading sources of GHG emissions for non-CO2 GHGs are agricultural practices like the use of fertilizer, soil tillage, pesticides, irrigation practices, and harvesting.
In evaluating the environmental factor, the use of land prior to the production of biofuel plays a significant role. If forest or grassland are used for the conversion of biofuel, then the reduction of GHG emissions is markedly affected.

Lifecycle Analyses (LCA's)
Sustainability of biomass-based biofuel is increasingly measured via lifecycle analyses (LCAs). All the phases—input and output data (biomass production, feedstock storage and transportation, biofuel production, and transportation and final use)—of the product's lifecycle are required in an LCA. All output data are accounted for, including both leaked and captured gases and by-products.
However, in an LCA the results may vary considerably regarding the environmental impact of biofuel production and consumption because it mostly depends on the assumption of the main parameters.
As you can see from the above statements, the environmental sector is very diverse and includes a wide range of unique companies, covering subjects such as:-
- Power generation (using biomass, waste to energy, etc)
- Product recycling
If we concentrate on recycling in this sector, we can see that there three main types of recycling: mechanical, energy and chemical. Every single type is subdivided into minor categories but understanding them gives us a better idea of how the world processes most of its recyclables.
Recycling Process
Any of these three main recycling types involves three basic steps. First, they are collected and separated based on the waste, i.e., sorting residues by type of material and cleaning level; residue reuse, when the separated material goes through one of the three above-listed procedures and is then reverted back into raw material; and waste transformation, the final stage, when this raw material becomes a finished product again.
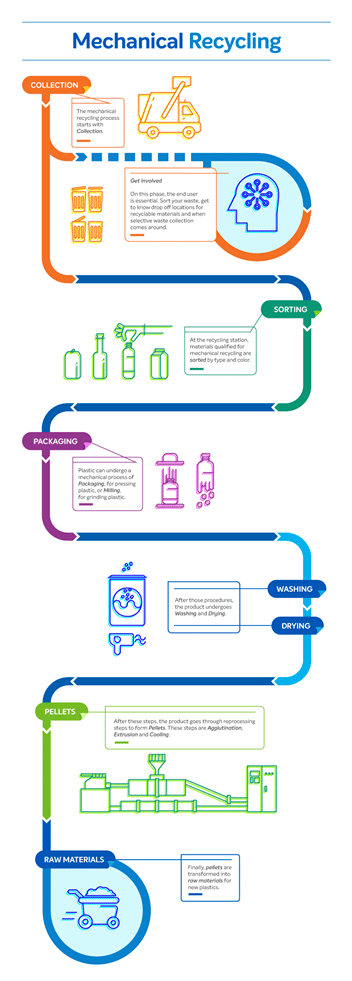
Our background in this sector has tended to concentrate on mechanical recycling process companies. Globally speaking, mechanical recycling is the most used method to give residues new usages, whatever they are.
Through this method, plastics & polymers – whether obtained from industrial scrap or domestic or commercial disposal – are mechanically transformed without changing their chemical structure, so they can be used to produce new materials.
Today, mechanically recycled plastics are used to make new packages, garbage bags, floors, hoses and car parts, among others. This is the most widely used technology for Polyolefins (PE and PP).
Mechanical Recycling Machinery
In this mechanical recycling process, we come across the following types if machinery which are critical to the process, such as:
- Trommels
- Crushers
- Grinders
- Extraction fans
- Conveyor drives
- Large hydraulic powerpacks and drives
- Pumps
- IVC Fans
- Bio filters
- Scrubbers
- Digesters
- Centrifuges
- AD plant
- Screens
Depending on what product is being produced these areas can sometimes be designated a hazardous area (ATEX). DMS have the equipment and expertise to operate and work in these locations / environments.